Dry port concept
Dry port concept is a way to improve intermodal transport system's cost-efficiency and environmental friendliness.
Dry port concept is a rather recent concept that aims at increasing cost-efficiency and environmental friendliness of transportation system. It has been researched since the late last century, although the most dry port researc is conducted during the last five or ten years.
Roso (2009b, p.308) has defined the dry port concept as:
'The dry port concept is based on a seaport directly connected by rail to inland intermodal terminals, where shippers can leave and/or collect their goods in intermodal loading units as if directly at the seaport. In addition to the transshipment that a conventional inland intermodal terminal provides, services such as storage, consolidation, depot, maintenance of containers and customs clearance are also available at dry ports.'
In the dry port concept majority of freight is transported by rail from seaport to inland intermodal terminals, which are called dry ports and vice versa. Only the final leg of transportation is accomplished by road i.e. main transport type of dry port concept is rail. The dry port concept is a way to improve the capacity and cost-efficiency of a transport system; especially seaport's inland access. The dry port concept also improves transport system's environmental friendliness. The concept decreases external costs of the transport system, since railroad is environmentally friendlier transport mode than road. There are also other benefits of the dry port concept such as reduced congestion, noise and accidents at the whole transportation system. (REFERENCE ROSO?) (Roso, 2009a & 2009b; Roso et al., 2008)
The dry port concept is an intermodal transportation system. The dry port itself is an inland intermodal terminal with additional services located inland. It is directly connected by rail to seaport or in some cases two or more seaports. In a dry port concept the maximum possible amount of freight transportation is accomplished by rail between the dry port and the seaport. Only the final leg of the door-to-door transportation is carried out by road transport. In an optimal dry port implementation the whole freight transportation between seaport and dry port is carried out by rail. However, that is usually not possible due to capacity of rail connection. (Roso, 2009a, b)
The dry port offers value-creating services (e.g. consolidation, storage, depot, maintenance of containers and customs clearance) to actors which operate within the transportation system i.e. there is a whole range of administrative activities that could be moved inland with implementation of a dry port. Outsourcing activities from seaport to dry port relieves seaport, and hence seaport can concentrate in its core tasks and competencies.
According to most recent literature, dry ports are categorized into three different categories. They are close dry port, mirrange dry port and distant dry port. The difference in different dry port are the location from seaport. Close dry ports are located approximately 50 kilometers from seaport. Distant dry ports are located 500 km or over from seaport. Midrange dry ports are situated between close and distant dry ports. All the different dry port categories are presented in Figure 1 below. In addition, Figure 1 illustrates a comparison of a conventional hinterland transport and an implemented dry port concept.
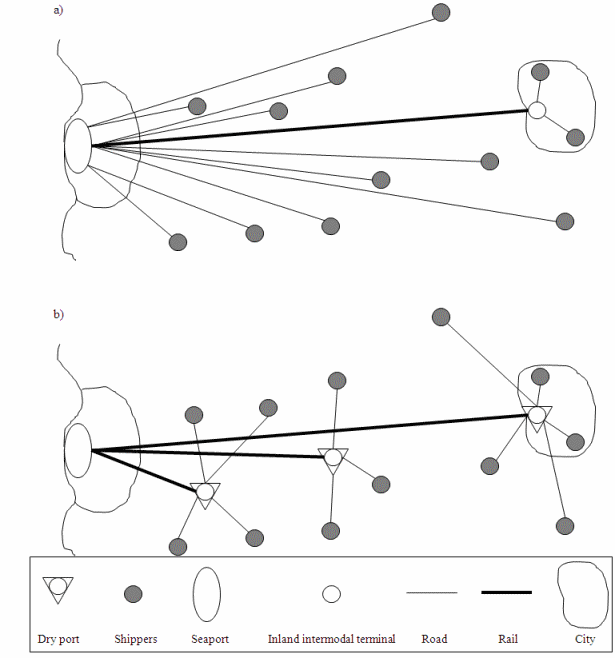
Figure 1. Comparison of a conventional hinterland transport and an implemented dry port concept.
From Figure 1 it can be seen that the distance travelled by road transport shortens, because shippers can use the nearest dry port instead of always carrying freight to seaport city. Also the number of freight connections to seaports lessens. There are 10 road connections and one rail connection to and from seaport in the upper part of Figure 1. With dry port solutions there are only three rail connections to and from seaport. Dry ports relieve the transportation system.
Different benefits that dry ports create according to literature are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1. Impacts generated by dry ports for the actors for the transportation system.

